Kostas Tingos
Projects
Recent advances in zero-shot learning have enabled the use of paired image-text data to replace structured labels, replacing the need for expert annotated datasets. Models such as CLIP-based CheXzero utilize these advancements in the domain of chest X-ray interpretation. We hypothesize that domain pre-trained models such as CXR-BERT, BlueBERT, and ClinicalBERT offer the potential to improve the performance of CLIP-like models with specific domain knowledge by replacing BERT weights at the cost of breaking the original model’s alignment. We evaluate the performance of zero-shot classification models with domain-specific pre-training for detecting low-prevalence pathologies. Even though replacing the weights of the original CLIP-BERT degrades model performance on commonly found pathologies, we show that pre-trained text towers perform exceptionally better on low-prevalence diseases.
Links: Paper (arXiv)

Links: Paper (arXiv)

In this work, we explore the combination of generalized and specialized pre-training to improve zero-shot pathology classification in chext x-rays. This combination of pre-training methods, which we call CheXmera, replaces the image or text tower of a general baseline with a locked or unlocked specialized pre-trained model. We find that strong image pre-training alone leads to the biggest increase in performance over the baseline, but pre-trained text towers remain valuable as they demonstrate extremely strong performance with pathologies that are rarely mentioned in the alignment training dataset. We also discover that unlocking these specialized towers during the tuning does not seem to degrade the rich pre-trained embedding space and is instead beneficial across both the image and text modalities.
Links: Paper, GitHub

Links: Paper, GitHub

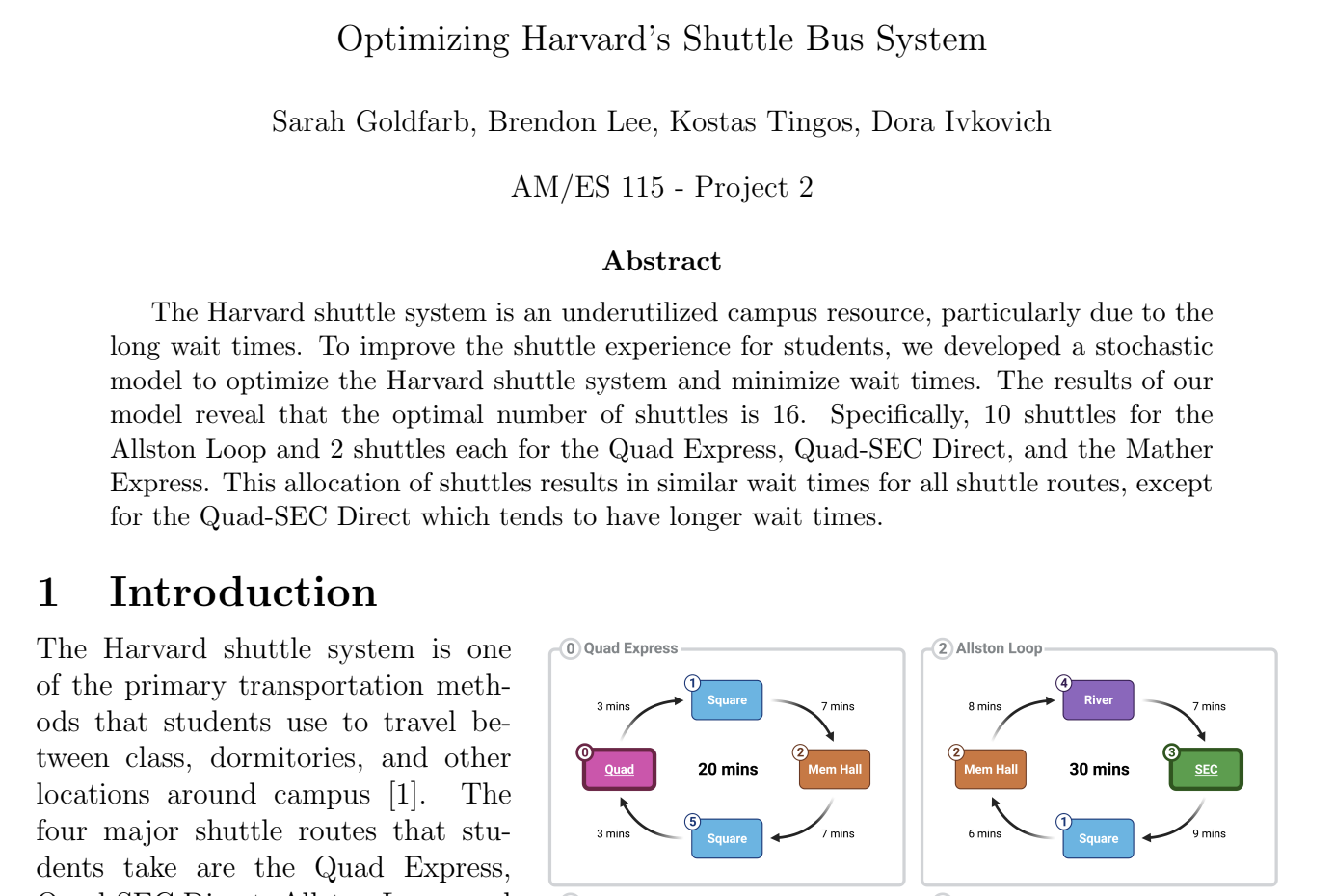
Acetaminophen (APAP) is one of the most commonly taken medications in the world and accounts for nearly half of acute liver failure cases in the US. Thus, we sought to model the metabolism of APAP and the formation of its toxic product. Specifically, we created a system of differential equations to model the three most important pathways in APAP metabolism.
Links: Report, Colab
Links: Report, Colab

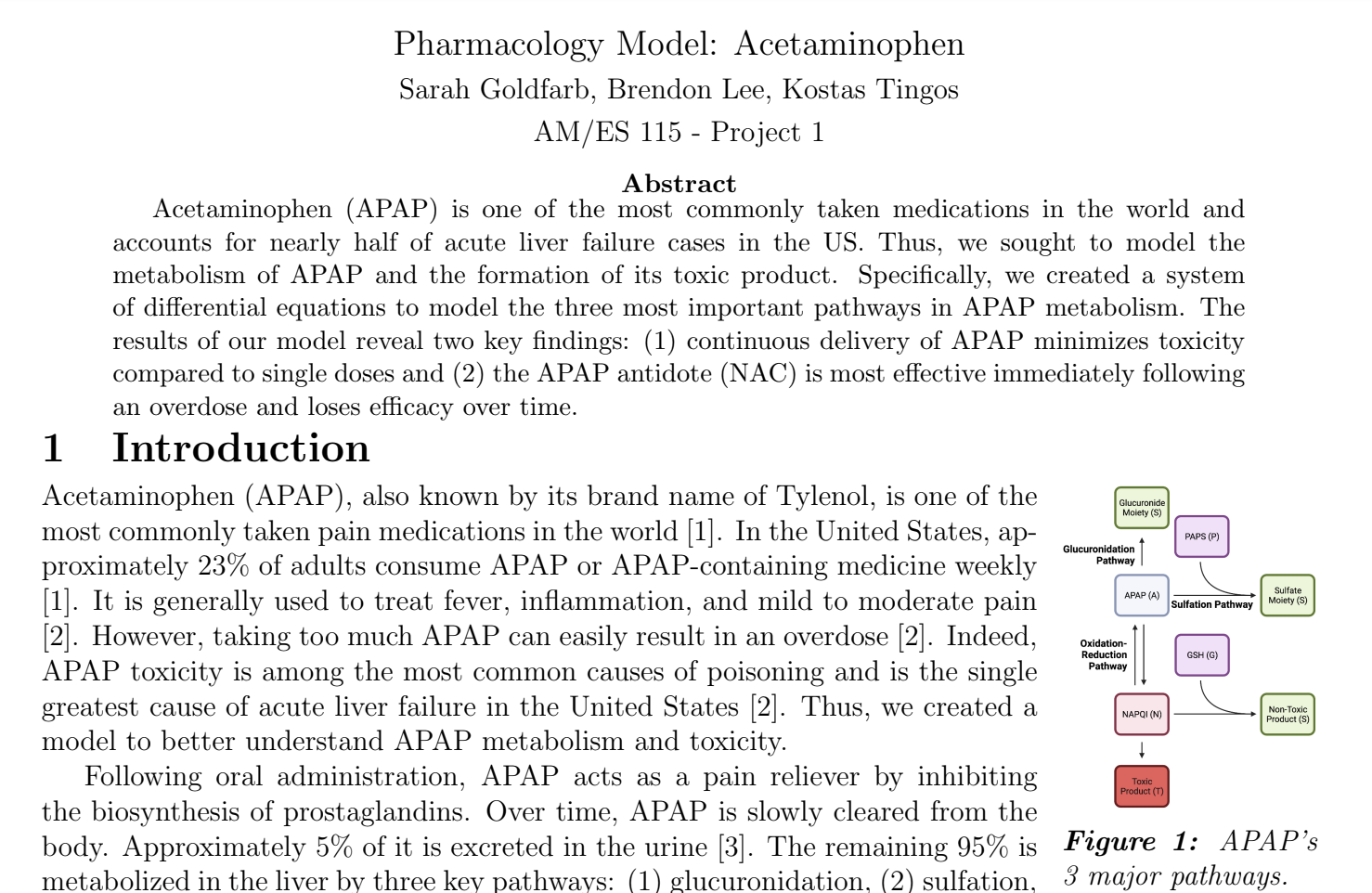
This Flask web application allows users to create an account and keep track of their reading. Users can log individual books and how many pages they've read on a given day. They can also see a graphic for how much they've been reading over the past week and book suggestions based on what others have logged.
Links: GitHub
Links: GitHub
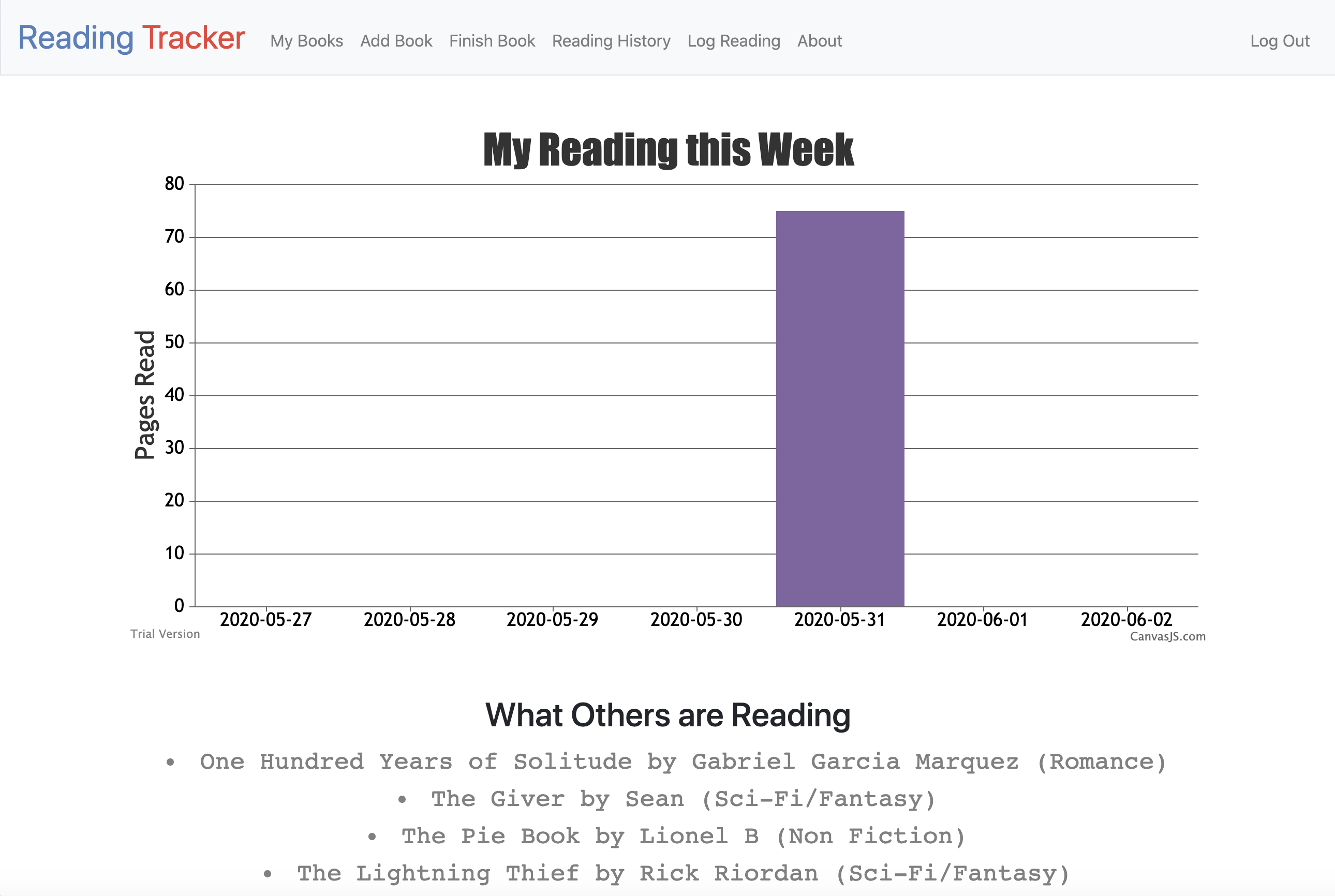
This Flask web application lets you play Tic-Tac-Toe with a friend. You can restart the game at any time, undo a move, and see a full history of all the moves after the game is complete.
Links: GitHub
Links: GitHub

This is a React application where users can make and study flashcards. You create and remove flashcards in the editor, and then you can study them in the viewer.
Links: GitHub
Links: GitHub